Salesforce Deployment Automation Checklist for Production Releases (2026)
Salesforce deployment automation checklist is becoming an essential tool for modern Salesforce teams. As release cycles accelerate and environments grow more complex, organizations must follow structured, repeatable processes to avoid production incidents.
Without a clear checklist, even automated pipelines can fail. Missing dependencies, broken permissions, incomplete testing, and configuration drift remain common causes of release outages.
Platforms such as ZUPPIO help teams convert deployment checklists into automated workflows with built-in validation, rollback, and governance controls.
If you are just getting started, we recommend reading our complete Salesforce deployment automation guide to understand how automated release pipelines work in practice.
This article provides a practical, step-by-step checklist that ISVs and enterprises can use in 2026 to prepare safe, scalable, and audit-ready production releases.

Why You Need a Deployment Automation Checklist
Production deployments carry high operational risk. Even minor configuration errors can disrupt business processes, integrations, reporting, and customer operations.
A Salesforce deployment automation checklist helps teams standardize their release workflows and reduce dependency on individual engineers.
When releases rely on personal experience instead of defined procedures, quality becomes inconsistent and difficult to scale.
Common Risks Without a Checklist
Teams that rely on informal processes often experience:
- Undetected metadata conflicts
- Incomplete profile and permission updates
- Failing integrations
- Broken automation rules
- Delayed incident response
- Limited audit visibility
A structured checklist transforms deployments from risky events into predictable, repeatable operations.
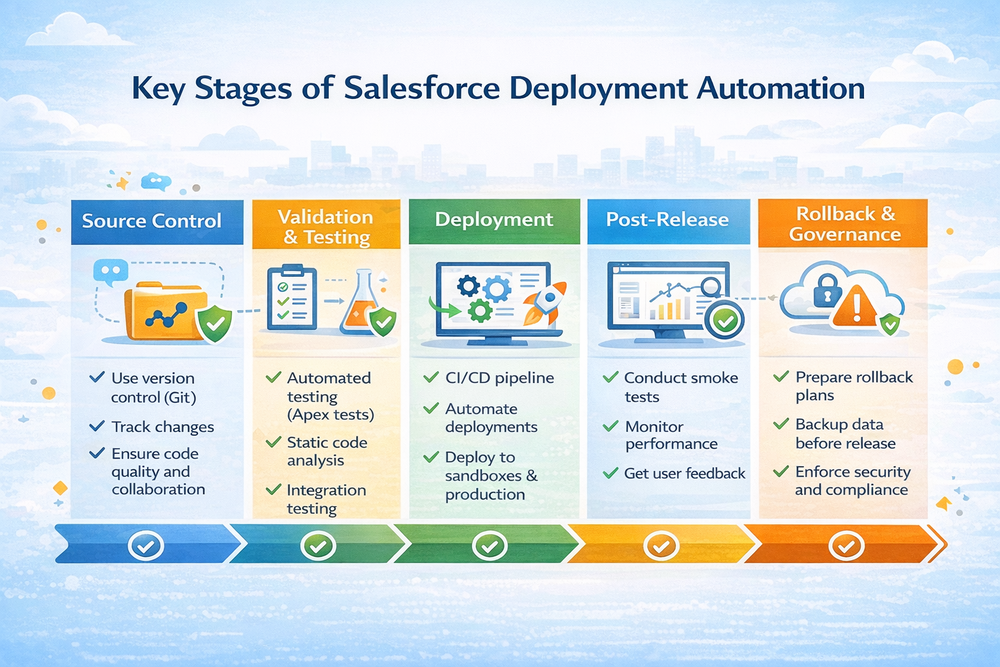
How This Salesforce Deployment Automation Checklist Works
This checklist is organized into six operational phases:
- Pre-deployment preparation
- Automated validation
- Controlled execution
- Post-deployment automation
- Rollback readiness
- Governance and audit controls
Each phase builds on the previous one and enforces quality gates before releases progress further.
Instead of treating deployments as isolated events, this model creates a continuous, governed release system.
Phase 1 — Pre-Deployment Preparation
Preparation is the foundation of reliable automation. Most deployment failures originate from incomplete or rushed pre-release activities.
Source Control Readiness
Before every release, ensure that:
- All metadata and configuration files are committed
- No unresolved merge conflicts exist
- Branches have passed peer review
- Release tags or versions are defined
Use structured Git version control workflows to maintain reliable change history.
Environment Alignment
All environments must share consistent configuration baselines:
- API versions aligned
- Feature settings synchronized
- Connected apps configured
- Integration credentials verified
Misaligned environments invalidate validation results and increase deployment risk.
Dependency Review
- Referenced components exist in target orgs
- Managed package versions are compatible
- External systems are available
- Cross-object dependencies are resolved
Security and Access Review
- Profiles reviewed
- Permission sets updated
- Sharing rules verified
- Integration users validated
Release Scope Validation
- Scope documented
- Stakeholders informed
- Change tickets approved
- Rollback scenarios defined
ZUPPIO helps teams standardize these preparation checks as reusable pre-deployment automation workflows.
Phase 2 — Automated Validation
Validation acts as the primary safety mechanism in deployment automation.
Automated validation identifies issues before production is affected and prevents unstable releases from progressing.
In Salesforce, this phase typically combines Metadata API check-only deployments with automated Apex test execution.
With ZUPPIO, validation rules, dependency checks, and test execution are enforced automatically across all target environments.
Advanced Salesforce CI/CD validation and rollback workflows help teams detect failures early.
Validation Checklist
- Component dependencies verified
- Metadata API validation completed
- Apex tests passed
- Permission access validated
- Deployment impact assessed
Phase 3 — Controlled Deployment Execution
Execution must follow standardized pipelines and approval processes.
Unstructured deployments increase the probability of human error and inconsistent outcomes.
Deployment Controls
- Maintenance windows confirmed
- Technical approval received
- Business approval documented
- Rollout plans defined
- Support teams notified
Scalable Salesforce deployment tools enable parallel execution across multiple environments.
ZUPPIO orchestrates multi-stage deployment automation pipelines with built-in approval gates and execution tracking.
Phase 4 — Post-Deployment Automation
Many release failures occur after metadata is deployed, when configurations remain incomplete.
Post-deployment automation ensures operational consistency.
Post-Release Tasks
- Page layout synchronization
- Picklist and reference data updates
- Data fixes
- Apex script execution
- Job scheduling
- System monitoring
ZUPPIO automates these tasks through integrated post-deployment automation workflows.
When incidents occur, teams rely on automated rollback procedures to stabilize environments.
Phase 5 — Rollback and Recovery Readiness
Rollback is not a contingency plan. It is a core automation capability.
Every production release should be reversible.
Recovery Checklist
- Versioned deployment packages available
- Metadata backups verified
- Data recovery plans tested
- Recovery scripts prepared
- Incident response procedures documented
ZUPPIO maintains detailed deployment execution history and versioned packages for fast recovery.
Phase 6 — Governance and Audit Controls
Automation must support compliance and accountability.
Without governance, automation becomes difficult to manage at scale.
Governance Requirements
- Deployment history recorded
- Release owners assigned
- Approval records retained
- Audit reports available
- Access policies enforced
ZUPPIO provides centralized audit trails and governance controls for enterprise environments.
Production Deployment Checklist Summary
Before every production release, teams should confirm that:
- Source control is clean and reviewed
- Environments are aligned
- Validation has passed
- Approvals are documented
- Post-deployment tasks are automated
- Rollback plans are ready
- Governance records are complete
This summary can be used as a final release readiness gate.
How ZUPPIO Automates This Checklist
ZUPPIO converts this checklist into executable workflows.
Through centralized automation and integrated Salesforce DevOps features, teams can manage:
- Validation pipelines
- Deployment orchestration
- Post-release automation
- Rollback procedures
- Governance reporting
All steps are executed consistently across environments and release cycles.
Real-World Example: Preventing a Failed Release
An independent software vendor managing dozens of customer organizations experienced frequent incidents due to inconsistent validation and manual recovery processes.
After adoption:
- Release failures declined significantly
- Support workload decreased
- Deployment predictability improved
- Compliance reporting became simpler
Common Mistakes When Using Deployment Checklists
Manual Overrides
Bypassing automated approval and validation gates weakens system reliability.
Skipping Validation
Incomplete testing remains a leading cause of production outages.
Missing Rollback Planning
Delayed recovery extends downtime and customer impact.
Weak Documentation
Undocumented processes limit scalability and onboarding.
Conclusion
A Salesforce deployment automation checklist is not simply a reference document. It is an operational framework that enables scalable, secure, and compliant releases.
When supported by centralized automation platforms such as ZUPPIO, this checklist becomes a living system that evolves alongside organizational requirements.
As Salesforce expands AI-assisted development and automation capabilities, structured release governance becomes even more critical.
What is a Salesforce deployment automation checklist?
It is a structured framework for validating, executing, and governing production releases through automated workflows.
How often should the checklist be updated?
It should be reviewed after major Salesforce platform updates, architectural changes, or regulatory requirements.
Is this checklist useful for ISVs?
Yes. It is designed for organizations managing multiple customer organizations and frequent package upgrades.
Can this checklist be fully automated?
Yes. Modern DevOps platforms can convert checklist steps into reusable deployment workflows.
How does ZUPPIO support this process?
ZUPPIO automates validation, execution, rollback, and governance to ensure consistent checklist enforcement.