Salesforce CI/CD Best Practices: Validation, Automation, and Rollback Workflows
CI/CD has become a crucial component of modern Salesforce development. As organizations grow and the number of environments increases, manual deployment processes no longer meet the standards of speed, stability, and predictability required by high-performing teams.
Salesforce CI/CD is more complex than traditional DevOps pipelines because metadata, org-specific configuration, and subscriber-editable components introduce unique risks. Without proper validation and rollback strategies, even a single deployment can disrupt production or create inconsistencies across multiple environments.
This article outlines the core best practices for Salesforce CI/CD, with a special focus on validation-first workflows, automation, and rollback strategies. It also highlights how tools such as ZuppIO simplify and strengthen these processes at scale.

1. Why CI/CD Matters in Salesforce
While traditional software pipelines work with source-controlled codebases, Salesforce development spans:
- Metadata with dependencies
- Profiles, layouts, and other org-specific elements
- Multiple sandboxes and parallel teams
- Managed package releases
- Client environments (especially for ISVs)
Manual deployment approaches, such as Change Sets, do not scale and frequently lead to:
- Missing components
- Deployment inconsistencies
- Incomplete permissions
- Configuration drift
- Failed releases
CI/CD introduces structure, predictability, and repeatability — dramatically reducing manual work and human error.
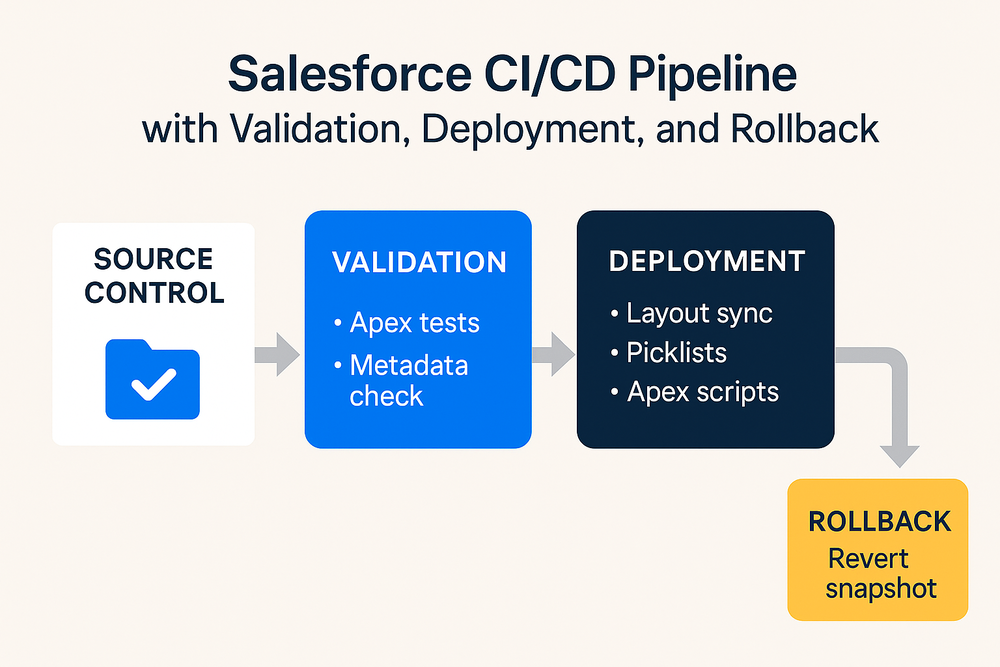
2. Validation-First Deployment Workflows
One of the most important best practices in Salesforce CI/CD is to validate changes before applying them. Validation ensures that:
- Metadata dependencies are met
- Apex tests pass
- Profiles and permissions align
- Target orgs are ready for deployment
This is especially critical for teams managing many environments or ISVs distributing managed package updates. Validation provides early insight into which orgs will fail and why.
Validation in ZuppIO
ZuppIO integrates validation as a core workflow step. Before applying changes at scale, teams can run a validation-only deployment on dozens or hundreds of orgs simultaneously. The system identifies:
- Missing components
- Metadata conflicts
- Failing tests
- Version mismatches
This reduces deployment risk and ensures predictable releases.
3. Automation Across the Full Deployment Lifecycle
A complete Salesforce CI/CD pipeline extends far beyond metadata deployment. It includes:
a) Metadata delivery from source control
- Git-based workflows
- Review and merge processes
- Version tracking
b) Deployment execution
- Automated deployments triggered by pull requests
- Webhooks connecting GitHub or Bitbucket
- Multi-org execution
c) Post-deployment automation
- Layout updates
- Picklist synchronizations
- Permission adjustments
- Apex initialization scripts
- Configuration updates
- Managed package upgrades
These tasks are still done manually in many teams — slowing down releases and increasing risk.
Automation in ZuppIO
- Git webhook-driven deployments
- Mass metadata deploys
- Post-install updates (layouts, picklists, profiles)
- Execute Anonymous Apex across many orgs
- Multi-org CI/CD pipelines without Jenkins
This eliminates repetitive work and provides consistency across environments.
4. Rollback Strategies for Salesforce Deployments
Salesforce does not offer a native rollback mechanism. Restoring metadata manually after an issue is:
- Slow
- Inconsistent
- Error-prone
Teams need a reliable rollback strategy to maintain stability.
Rollback Best Practices
- Take snapshots or backups before each deployment
- Track changes at the component level
- Maintain a detailed deployment log
- Automate rollback steps
Rollback in ZuppIO
ZuppIO includes a built-in Revert feature that restores metadata to its previous version when deployment issues occur. Combined with validation and audit logs, this enables:
- Faster recovery
- Minimal downtime
- Consistent environments
Rollback becomes part of the standard workflow, not an emergency procedure.
5. Governance, Auditability, and Transparency
A robust CI/CD process must ensure:
- Visibility into every deployment
- Traceability of who deployed what and when
- A complete audit trail
- Version history and environment comparison
ZuppIO centralizes:
- Deployment history
- Validation logs
- Revert actions
- Multi-org audit trails
This supports governance, compliance, and internal quality control.
Conclusion
Modern Salesforce teams cannot rely on manual deployments or fragmented CI/CD tooling. Best practices — validation-first workflows, automation, post-deployment updates, and reliable rollback — are essential for stability and scalability.
ZuppIO provides a unified CI/CD orchestration platform that integrates validation, automation, and rollback into a single workflow. This empowers Salesforce teams to deliver faster, safer, and more predictable releases without relying on scripts, CLIs, or dedicated DevOps engineers.
What is Salesforce CI/CD?
Salesforce CI/CD is a structured process for automating metadata changes, testing, and deployments across environments using validation, automation, and monitoring.
Why is validation important in Salesforce deployments?
Validation ensures dependencies, tests, and permissions align before deployment, reducing risk and preventing failed releases.
How do you automate Salesforce deployments?
Automation is achieved through metadata pipelines, git-triggered deployments, and post-deploy steps such as layouts, picklists, and Apex scripts.
Is there a rollback option in Salesforce CI/CD?
Salesforce has no native rollback feature, but tools like ZuppIO offer automated rollback to restore previous metadata states.
What makes ZuppIO useful for CI/CD?
ZuppIO provides multi-org validation, automated deployments, post-deploy updates, and one-click rollback — without scripts or Jenkins.